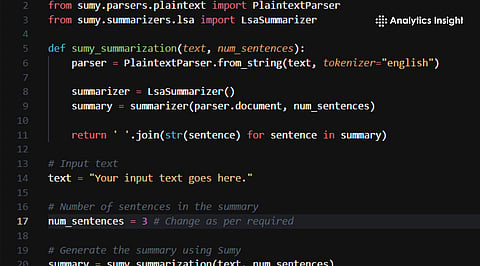

Python NLP makes text summarization faster and easier for large documents.
Extractive methods are more accurate, while abstractive methods are more readable.
Hybrid summarization reduces errors and improves overall summary quality.
Text summarization is one of the most popular use cases of Natural Language Processing. A massive amount of textual data is created through news articles, research papers, emails, customer reviews, legal documents, and meeting notes. It can be difficult to read and comprehend all of this content.
With text summarization, you can convert long-form content into short and meaningful summaries and save time and effort. While these models have become more advanced, they still face difficulties like factual errors, missing key points, and bias. This article explores the best way to summarize text using Python NLP and overcome these issues.
There are two methods of text summarization:
Extractive Summarization: The model selects the most important sentences from the original text and copies them exactly as they appear. This method is fast and reliable, and it rarely changes facts. Extractive summarization is used in legal, financial, and compliance-related content. The disadvantage of depending on this method is that the summary can feel less natural and slightly repetitive.
Abstractive Summarization: The Natural Language Processing model creates a summary using new words and sentence structures. It functions similarly to how humans summarize content. The output is usually shorter and easier to read. However, according to studies conducted in 2025-2026, abstractive models are known to generate incorrect details when summarizing long or technical documents.
To reduce these problems, many modern systems now combine both approaches.
Python is the top language that developers prefer for NLP tasks, as it is easy to learn and has strong library support. A standard Python NLP setup includes updated versions above 3.10 that support deep learning and long-text handling.
Popular NLP tools focus on:
Fast text processing
Support for large language models
Better handling of long documents
Improved performance on GPUs
These updates help summarize longer content quickly, but proper configuration is important for good results.
Text preprocessing is crucial for summary quality. If the input text is poor, the output summary will also be weak.
Common preprocessing steps include:
Removing extra spaces, broken lines, and symbols
Deleting repeated titles, menus, and footer text
Making sure sentences are complete and readable.
Splitting text into proper sentences
Sentence splitting is especially important. Simple punctuation rules often fail when text contains abbreviations, numbers, or technical terms. NLP-based sentence detection improves accuracy and makes summaries more stable.
Also Read - Charting the Path of Language Intelligence: Innovations in Natural Language Processing
Extractive summarization is usually the first step in many pipelines. It works by finding the sentences most relevant to the main topic.
This method relies on:
Word frequency and importance
Similarity between sentences
Position of sentences in the document
For example, in news articles, early sentences usually carry key information. In reports, summary sections and headings are more important. Extractive summaries are easy to verify because every sentence exists in the original text, making them safer for business use.
Abstractive summarization uses deep learning models trained on large datasets. These models understand context, meaning, and relationships between ideas.
Abstractive models are better at:
Writing fluent summaries
Reducing redundancy
Handling conversational or informal text
However, issues still exist. Research published in late 2025 shows that long-document summarization suffers from missing middle sections and incorrect number rewriting. This emphasizes the need to review abstractive summaries carefully.
Document length is a major challenge in summarization. Many models have limits on how much text they can process at once.
Chunking is a common solution that involves breaking long documents into smaller parts. Each part is summarized separately, and the synopses are then merged into a single final summary. This approach improves coverage and reduces memory issues.
Recent evaluations also show that chunk-based summarization reduces positional bias, which occurs when models focus too much on the beginning or end of a document.
Previously, users focused more on word-overlap scores for summary evaluation. However, now it depends on meaning and correctness.
Good evaluation practices include:
Checking if key facts are preserved
Making sure names, dates, and numbers are correct
Comparing the summary meaning with the original text
According to recent studies, summaries can sound correct while being factually wrong. This highlights the need for human review or the addition of automatic fact-checking in production systems.
Also Read - Python vs Other Programming Languages: Which Is Best in 2026?
Many teams now use hybrid workflows for real-world applications. These workflows reduce text using extractive summarization, then apply abstractive models to rewrite the content more smoothly.
This method:
Reduces hallucinations
Improves accuracy
Keeps summaries readable
In sensitive industries like healthcare, law, and finance, extractive summaries are still preferred, while abstractive summaries are used for marketing, blogs, and internal reports.
Text summarization with Python NLP involves combining good preprocessing, extractive baselines, abstractive models, and quality checks. With further research, the latest models are expected to be more accurate, factual, and better at handling very long documents.
1. What is text summarization in NLP?
Text summarization is the process of condensing long text while preserving its main meaning.
2. Why is Python used for text summarization?
Python is simple to use and has strong NLP libraries for summarization tasks.
3. What is the difference between extractive and abstractive summarization?
Extractive summarization copies key sentences, while abstractive summarization rewrites them.
4. Is abstractive summarization fully accurate in 2026?
Abstractive models are improved but can still make small factual mistakes.
5. How are long documents summarized effectively?
Long documents are split into smaller parts and summarized step by step.
